
It can often point out areas that are dragging the profitability of a company down and therefore need improvement. The effectiveness of new management plans, new products, and changes in operational procedures can all be determined by analyzing accounting ratios. A regular review of your company’s financial ratios can help you focus on areas that may need improvement.
Understanding an Accounting Ratio
Hypothetical illustrations may provide historical or current performance information. Use the Leverage of Assets Calculator above to calculate the leverage of assets and Du Pont ratios from your financials statements. Leverage of Assets measures the ratio between assets and owner’s equity of a company. The Dividend Payout Ratio is the percentage of earnings that are paid out to shareholders.
What Are Shares Outstanding?
Earnings not paid to shareholders are expected to be retained by the company and invested in further operations. The Dividend Yield shows how much a company pays out in dividends each year relative to its share price. In the absence of any capital gains, the dividend yield is the return on investment for a stock.
Financial Ratios Calculator
It is easy to see how a business is performing and compare it to other periods. Leveraged Assets Contribution to NI is the percentage of the pretax income that is provided by management’s use of debt to fund assets. Income from Unleveraged Assets is the income generated by the assets funded by shareholders equity and operations. Use the Asset Turnover (Du Pont) how to get started with invoicing for your photography business Calculator to calculate the asset turnover and Du Pont ratios from your financial statements. Use the Profit Margin (Du Pont) Calculator above to calculate the profit margin and Du Pont ratios from your financial statements. The Debt to Tangible Net Worth Ratio is a measure of a company’s financial leverage to the tangible asset value of owner’s equity.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. This is because they only summarize what has happened in a business using certain accounting conventions. This is used for forecasting and to set the expected sales every day over an evenly distributed sales forecast. Days Receivables indicates the average number of days that receivables are outstanding.
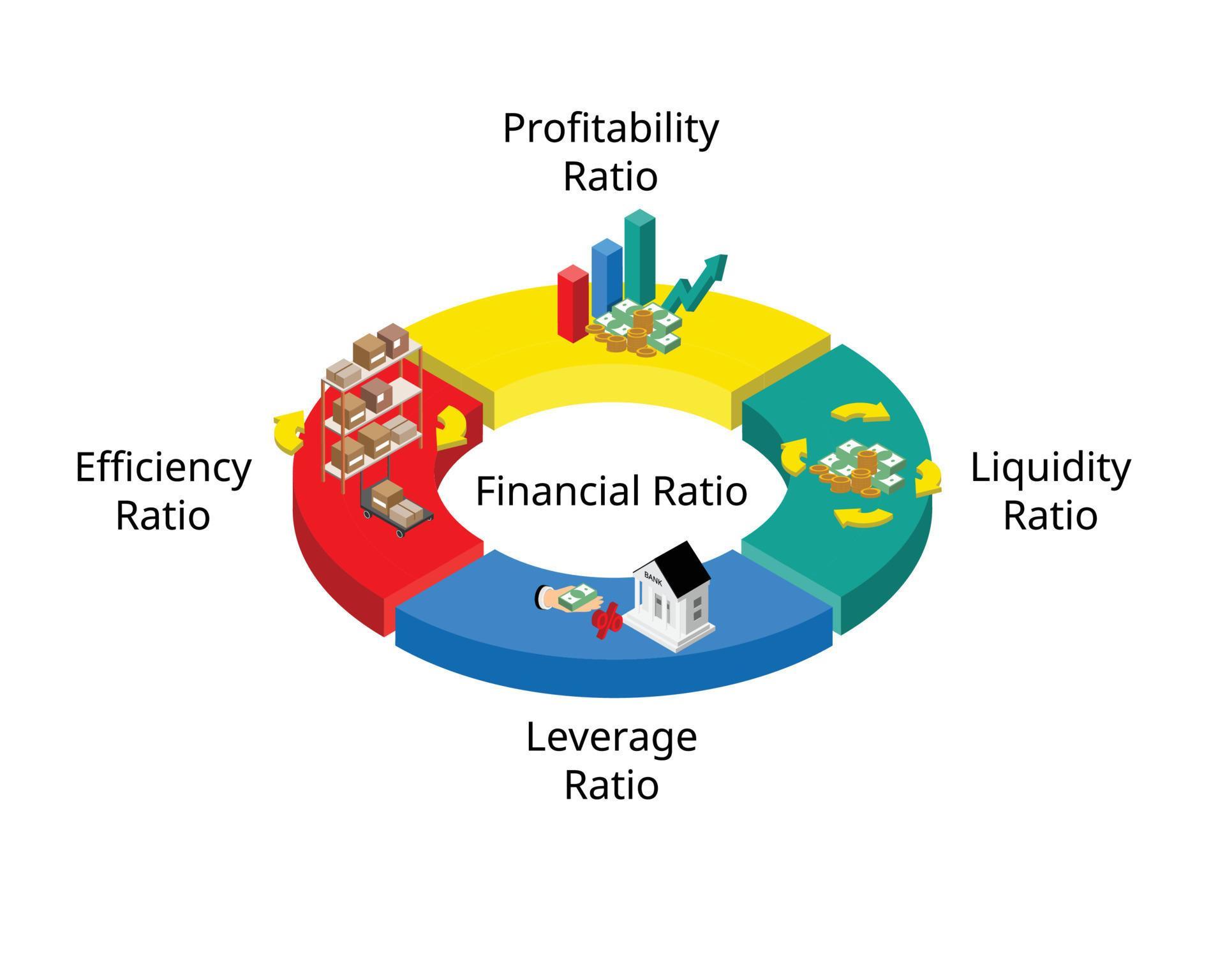
Comparative ratio analysis can be used to understand how a company’s performance compares to similar companies in the same industry. For example, a company with a 10% gross profit margin may be in good financial shape if other companies in the same sector have gross profit margins of 5%. However, if the majority of competitors achieve gross profit margins of 25%, that’s a sign that the original company may be in financial trouble. Liquidity ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off short-term liabilities with current assets like cash and equivalents, accounts receivable and inventory. The three most common types of accounting ratios are debt ratios, liquidity ratios, and profitability ratios. Accounting ratios, also known as financial ratios, are used to evaluate a business’s financial performance and position.
- Accounting ratios provide a view of a company’s financial health but they’re only one viable tool when you’re assessing investments.
- It doesn’t involve one single metric; instead, it is a way of analyzing a variety of financial data about a company.
- Financial Statements are prepared by companies to demonstrate its financial activity to stakeholders.
- It is easy to see how a business is performing and compare it to other periods.
- To counter this limitation, investors also need to understand the variables behind ratios, what information they do and do not communicate, and how they are susceptible to manipulation.
It’s calculated by dividing a company’s net income by its revenues and is often used instead of dissecting financial statements to compare how profitable companies are. The Net profit margin ratio measures the net profit from the profit and loss account against revenue. The Net profit is calculated by taking the gross profit and deducting the expenses. Expenses include other running costs of the business, which do not relate directly to sales. Accounting ratios can provide an accurate assessment of the profitability of a company over the last quarter or fiscal year.
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations. Examples include Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio and Interest Coverage Ratio. Accounting ratios can be broadly classified as liquidity ratios, solvency ratios, profitability ratios, activity/efficiency ratios and coverage/leverage ratios. Analysis of Leverage is used to evaluate how effectively management is using borrowed funds to make a return for income. Typically, funds are raised by debt in order to enhance the return to shareholders.
Ratio analysis is usually rooted heavily with financial metrics, though ratio analysis can be performed with non-financial data. Every figure needed to calculate the ratios used in ratio analysis is found on a company’s financial statements. By entering different period figures into the calculator, it is easy to compare two periods. The profitability of a business is reported in the Profit and Loss or Income Statement.
They provide a way of expressing the relationship between one accounting data point to another and are the basis of ratio analysis. They also serve as a comparison toolbox to compare the firms’ performance to that of its peer in the same industry. Ratio analysis can be used to understand the financial and operational health of a company; static numbers on their own may not fully explain how a company is performing. Though this seems ideal, the company might have had a negative gross profit margin, a decrease in liquidity ratio metrics, and lower earnings compared to equity than in prior periods. This means the company is performing below its competitors in spite of its high revenue.